
Benefits of Maple Forest Production
THE MAPLE TREE AND MAPLE SYRUP PRODUCTION
The maple industry contributes to the environment by conserving forested areas and nurturing trees that capture and store carbon as well as promoting biodiversity.
Maple syrup production also contributes to the economic, social and cultural prosperity of tens of thousands of local, mostly rural people that produce it and send it to markets.
Ultimately, we love maple syrup for its great taste!
Pure maple syrup is a naturally delicious sweetener that can make you happy and enhance your favorite breakfast cereal, pancakes, crêpes and coffee. Maple syrup can also be added to recipes to replace sugar and to delicious homemade baked goods, smoothies and other drinks and salad dressings, and it has some unique nutritional qualities.

FOREST CONSERVATION AND BIODIVERSITY
Maple producers protect biodiversity by conserving a natural habitat that would otherwise be cut or developed for other land uses.
Maple forest management supports a diversity of plant, animal and insect species which contributes to a healthy ecosystem. Moreover, the sugar maple forest filters pollutants in the air and water, preserves soil, prevents disease, contributes to biological control and promotes plant and vegetation reproduction.
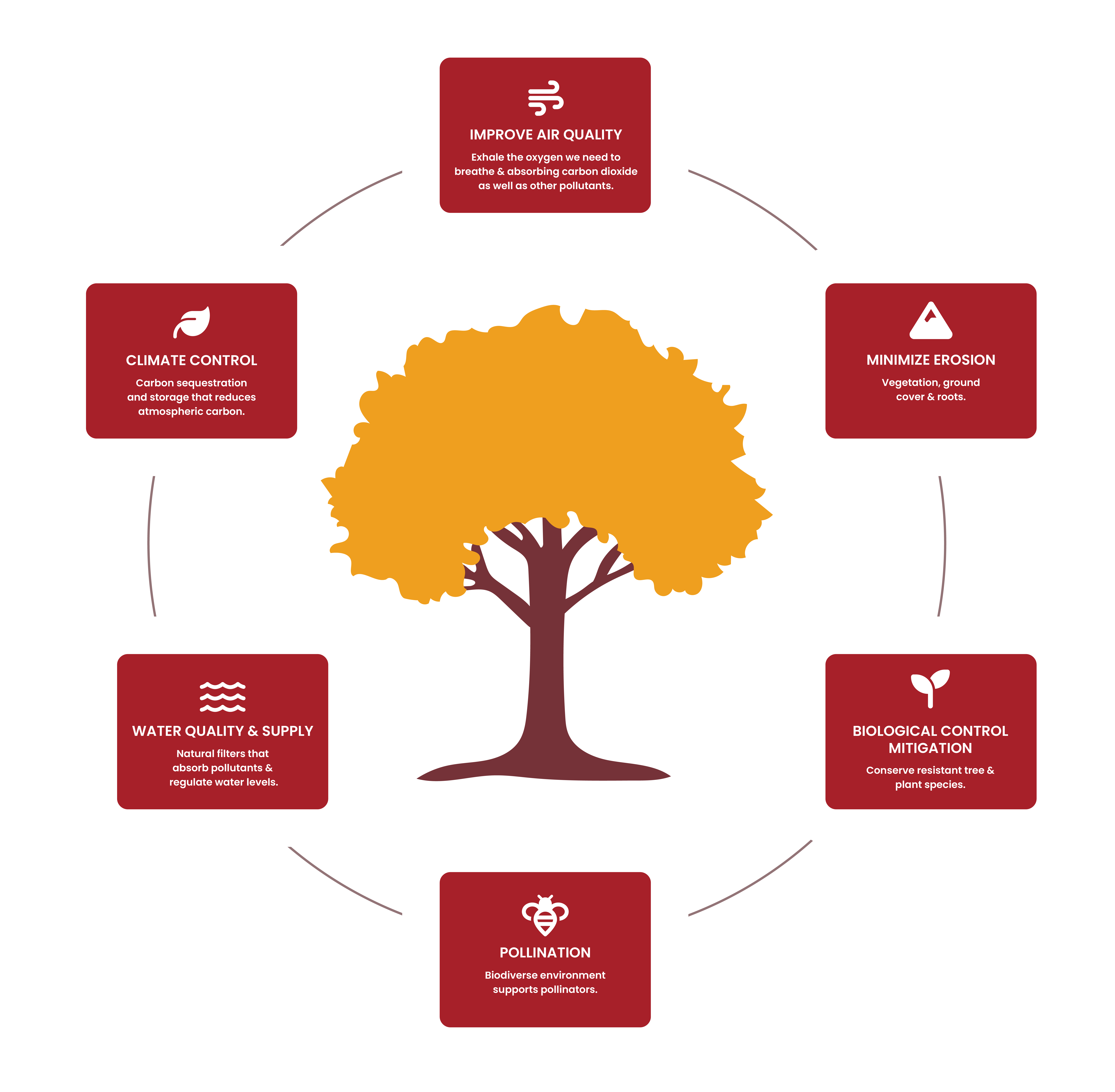
Why We Preserve the Maple Forest
The best form of carbon capture and sequestration is forestation, so preserving forested areas is critical to the earth’s future.
North American sugar bushes preserve forested areas and condition the environment by providing ecological benefits to the local environment and the earth. Maple woodlands contribute to a bio-diverse environment by providing a protected, natural habitat for many species of birds, animals and insects.
Benefits of Maple Forestry
Natural Sweetener
Brings a unique, inimitable, natural sweetener to consumers since maple syrup is one of most favored natural sweeteners that is added to hundreds of dishes.
Cornerstone of Culture
Benefits our people and economy because maple syrup production contributes to the economic, social and cultural prosperity of our world.
Supplies Full-Time Jobs
Maple sugar bushes are typically entrepreneurial businesses counted in the tens of thousands that employ approximately 18,300 full-time equivalent jobs. Maple processing, distribution, exporting and equipment manufacturing supply about 2,600 jobs alone.
Local to Global
Unlike many other food products, maple syrup production requires healthy, regenerating forests, which is a living benefit for the world. Maple products are exported all over the world but 100% of the world’s maple syrup is produced in the Northeastern regions of Canada and the U.S., and west to Ontario and Minnesota, as well as south down to Indiana.
See our full list of associates here.
Stimulates the Economy
The industry’s market value of production is about $1.4 billion CAD or $1.05 billion USD to the economy.
Nutritional Qualities
Maple syrup has excellent nutritional qualities including essential nutrients, minerals and antioxidants.
Forest-Farming Ecosystem
Supports a natural forest-farming ecosystem because maple syrup is produced in our forests, unlike many other food products that are produced in plowed and irrigated monoculture fields. Maple syrup production requires healthy, regenerating forests, which is a living benefit for the world.
Conservation of Land
Maple producers protect biodiversity by conserving a natural habitat that would otherwise be cut or developed for other land uses.
Filters Pollutants
The sugar maple forest filters pollutants in the air and water, preserves soil, prevents disease, contributes to biological control and promotes plant and vegetation reproduction. It preserves forested areas, which are critical to the earth’s future.

CULTURAL AND ECONOMIC ADVANTAGES: FROM LOCAL TO GLOBAL
Maple syrup production requires healthy, regenerating forests, which is a living benefit for the world.
Additionally, the maple forest farmers and other maple syrup producers downstream make a living from the natural forest. The Northeastern regions of Canada and the United States extending to Ontario and Minnesota in the Midwest altogether produce 100% of the world’s maple syrup.
The maple business is relatively small compared to other agrifoods. Unlike many other food products that are produced in plowed and irrigated monoculture fields, maple syrup is produced in an ever-changing natural forest ecosystem. It’s a unique forest product!

BOOSTING LOCAL ECONOMIES: THE IMPACT AND SIGNIFICANCE OF THE MAPLE SYrup INDUSTRY
Maple sugar bushes are typically entrepreneurial businesses counted in the tens of thousands that employ approximately 18,300 full-time equivalent jobs.
Maple processing, distribution, exporting, and equipment manufacturing jobs are estimated at 2,600. The industry’s market value of production is about $1.4 billion CAD or $1.05 billion USD to the economy. For generations now, maple sugaring continues to be an important traditional practice and a cultural mainstay that supports smaller local villages and towns throughout North America.
